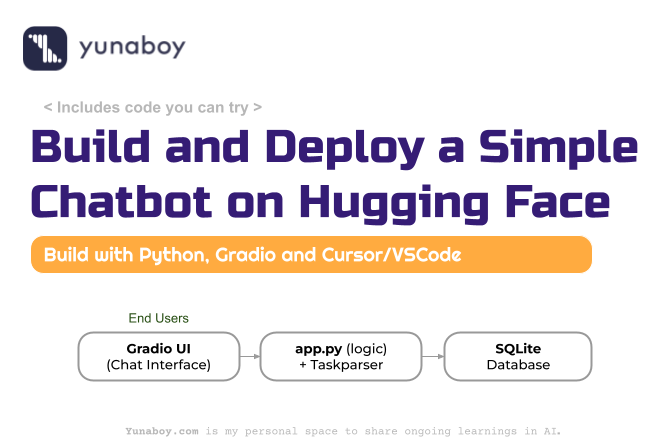
This article demonstrates building a simple Project Management Chatbot using Gradio, SQLite, and Groq AI integration. The implementation serves as a practical exploration of successfully publishing applications to Hugging Face Spaces with modern development tools and best practices.
The application enables natural language interaction for task management, status updates, and project reporting without requiring complex fine-tuning approaches. Development was conducted using Cursor IDE, though the codebase is compatible with any Python-supporting IDE.
Project Scope & Requirements
Primary Objective:
Create a conversational interface enabling project managers, team members, and leadership to manage tasks through natural language commands:
- Task Creation: “Create task: Fix login bug”
- Status Management: “Change status of Login bug to done”
- Information Retrieval: “Show tasks”, “Show users”, “Show stats”
- Access Control: Role-based visibility (
team_member,project_manager,management) - Performance Targets: 50% faster task creation, 90% capacity accuracy, 80% user adoption
Component Overview
- Frontend: Gradio Blocks for conversational UI
- Backend: Python application with database handlers and NLP parsing
- Storage: SQLite for persistent user and task data
- Intelligence: Regex-based parsing with Groq API enhancement
3. Development Environment Setup
# Create project directory and virtual environment
mkdir ProjectManagement_Chatbot && cd $_
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
# Define dependencies
cat > requirements.txt <<EOF
gradio==4.44.1
groq==0.4.1
EOF
# Install packages
pip install -r requirements.txt
Database Layer Implementation
The database layer provides persistent storage for users and tasks with automatic initialization and sample data population.
# app.py - Database initialization and management
import sqlite3
import os
from datetime import datetime
def init_database():
"""
Initialize SQLite database with proper schema handling.
Creates users and tasks tables, populates with sample data if empty.
"""
conn = sqlite3.connect('pm_chatbot.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
# Create users table with role-based access
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
username TEXT UNIQUE NOT NULL,
full_name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT UNIQUE NOT NULL,
role TEXT DEFAULT 'team_member',
is_active INTEGER DEFAULT 1,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
''')
# Create tasks table with status and priority tracking
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
title TEXT NOT NULL,
description TEXT DEFAULT '',
priority TEXT DEFAULT 'medium',
status TEXT DEFAULT 'todo',
assignee_id INTEGER,
created_by INTEGER,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
''')
# Insert sample data for demonstration
cursor.execute('SELECT COUNT(*) FROM users')
user_count = cursor.fetchone()[0]
if user_count == 0:
print("Creating sample data...")
# Sample users with different roles
sample_users = [
('john_pm', 'John Smith', 'john@company.com', 'project_manager'),
('sarah_dev', 'Sarah Wilson', 'sarah@company.com', 'team_member'),
('mike_dev', 'Mike Johnson', 'mike@company.com', 'team_member'),
('admin', 'Admin User', 'admin@company.com', 'management')
]
cursor.executemany(
'INSERT INTO users (username, full_name, email, role) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)',
sample_users
)
# Sample tasks with various states
sample_tasks = [
('Setup project repository', 'Create Git repo and initial structure', 'high', 'done'),
('Design user login system', 'Create authentication flow', 'high', 'in_progress'),
('Create task management API', 'Build REST API for tasks', 'medium', 'todo'),
('Write documentation', 'Create user guide and API docs', 'low', 'todo')
]
cursor.executemany(
'INSERT INTO tasks (title, description, priority, status) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)',
sample_tasks
)
conn.commit()
print("✅ Sample data created!")
conn.close()
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"Database initialization error: {e}")
conn.close()
return False
# Initialize database on application start
print("Initializing database...")
db_success = init_database()
Data Access Layer
Database interaction functions provide clean interfaces for CRUD operations with proper error handling.
def get_users():
"""Retrieve all users from database with error handling"""
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect('pm_chatbot.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT id, username, full_name, email, role FROM users')
users = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
return users
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error getting users: {e}")
return []
def get_tasks():
"""Retrieve all tasks ordered by creation date"""
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect('pm_chatbot.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT id, title, description, priority, status, created_at FROM tasks ORDER BY id DESC')
tasks = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
return tasks
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error getting tasks: {e}")
return []
def create_task(title, description="", priority="medium", status="todo"):
"""Create new task with validation and error handling"""
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect('pm_chatbot.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
if not description:
description = f"Task: {title}"
cursor.execute(
'INSERT INTO tasks (title, description, priority, status) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)',
(title, description, priority, status)
)
task_id = cursor.lastrowid
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return task_id
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error creating task: {e}")
return None
def update_task_status(title, new_status):
"""Update task status by matching title (case-insensitive)"""
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect('pm_chatbot.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(
"SELECT id FROM tasks WHERE LOWER(title)=LOWER(?) LIMIT 1",
(title,)
)
row = cursor.fetchone()
if not row:
conn.close()
return False
cursor.execute(
"UPDATE tasks SET status=? WHERE id=?",
(new_status, row[0])
)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return True
except Exception:
return False
def get_stats():
"""Generate project statistics with error handling"""
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect('pm_chatbot.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT COUNT(*) FROM users')
user_count = cursor.fetchone()[0]
cursor.execute('SELECT COUNT(*) FROM tasks')
task_count = cursor.fetchone()[0]
cursor.execute('SELECT status, COUNT(*) FROM tasks GROUP BY status')
status_counts = dict(cursor.fetchall())
conn.close()
return {
'total_users': user_count,
'total_tasks': task_count,
'task_breakdown': status_counts
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error getting stats: {e}")
return {'total_users': 0, 'total_tasks': 0, 'task_breakdown': {}}
Natural Language Processing Layer
The NLP layer handles command parsing with Groq AI enhancement for improved accuracy.
import re
class EnhancedTaskParser:
"""
Task parser with optional Groq API integration.
Falls back to regex-based parsing if API unavailable.
"""
def __init__(self):
# Check for Groq API key in environment (HF Spaces secrets)
self.groq_api_key = os.getenv('GROQ_API_KEY')
self.use_groq = self.groq_api_key is not None
if self.use_groq:
try:
from groq import Groq
self.groq_client = Groq(api_key=self.groq_api_key)
print("✅ Groq API initialized")
except ImportError:
print("⚠️ Groq package not available, using basic parsing")
self.use_groq = False
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ Groq API error: {e}, using basic parsing")
self.use_groq = False
def is_task_creation(self, text):
"""Detect task creation commands"""
keywords = ['create', 'add', 'new', 'make']
task_words = ['task', 'todo', 'work', 'job']
text_lower = text.lower()
return any(k in text_lower for k in keywords) and any(w in text_lower for w in task_words)
def is_status_update(self, text):
"""Detect status update commands"""
return bool(re.search(r"change status of .+ to (todo|in_progress|done)", text, re.IGNORECASE))
def extract_task_info(self, text):
"""Extract task information from natural language"""
# Try Groq API first if available
if self.use_groq:
groq_result = self.parse_with_groq(text)
if groq_result and groq_result.get('is_task_creation'):
return {
'title': groq_result.get('title', 'Untitled Task'),
'priority': groq_result.get('priority', 'medium'),
'success': True
}
# Fallback to basic regex parsing
title = self.extract_title_basic(text)
if title:
return {
'title': title,
'priority': self.extract_priority_basic(text),
'success': True
}
return {'success': False, 'error': 'Could not extract task title'}
def extract_title_basic(self, text):
"""Basic title extraction using regex patterns"""
patterns = [
r'["\'](.+?)["\']', # Quoted text
r'task\s*:\s*(.+?)(?:\s+for|\s+assign|$)', # After colon
r'(?:create|add|new)\s+(?:a\s+)?task\s+(.+?)(?:\s+for|\s+assign|$)' # After keyword
]
for pattern in patterns:
match = re.search(pattern, text, re.IGNORECASE)
if match:
return match.group(1).strip()
return None
def extract_priority_basic(self, text):
"""Extract priority level from text"""
text_lower = text.lower()
if any(word in text_lower for word in ['high', 'urgent', 'critical']):
return 'high'
elif any(word in text_lower for word in ['low', 'minor', 'simple']):
return 'low'
return 'medium'
def parse_status_update(self, text):
"""Parse status update commands"""
match = re.search(
r"change status of (.+?) to (todo|in_progress|done)",
text, re.IGNORECASE
)
if match:
return {
"title": match.group(1).strip(),
"new_status": match.group(2).lower()
}
return None
def parse_with_groq(self, text):
"""Enhanced parsing using Groq API"""
if not self.use_groq:
return None
try:
prompt = f"""Extract task information from: "{text}"
Return only valid JSON:
{{
"title": "task title here",
"priority": "high/medium/low",
"is_task_creation": true/false
}}"""
response = self.groq_client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Extract task info and return JSON only."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
],
model="llama3-8b-8192",
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=150
)
import json
result = json.loads(response.choices[0].message.content)
return result
except Exception as e:
print(f"Groq parsing error: {e}")
return None
# Initialize parser
task_parser = EnhancedTaskParser()
Response Formatting Layer
Display formatting functions create user-friendly representations of database content.
def format_users_display():
"""Format user list for chat display"""
users = get_users()
if not users:
return "No users found in database."
result = f"## 👥 Team Members ({len(users)})\n\n"
for user in users:
result += f"**{user[2]}** (@{user[1]})\n" # full_name, username
result += f"📧 {user[3]} | Role: {user[4]}\n\n" # email, role
return result
def format_tasks_display():
"""Format task list with status and priority indicators"""
tasks = get_tasks()
if not tasks:
return "No tasks found in database."
result = f"## 📋 Tasks ({len(tasks)})\n\n"
status_emoji = {'todo': '📋', 'in_progress': '🔄', 'done': '✅'}
priority_emoji = {'high': '🔴', 'medium': '🟡', 'low': '🟢'}
for task in tasks:
status = task[4] if task[4] else 'todo'
priority = task[3] if task[3] else 'medium'
s_emoji = status_emoji.get(status, '📌')
p_emoji = priority_emoji.get(priority, '⚪')
result += f"{s_emoji} **{task[1]}** {p_emoji}\n" # title
result += f"Status: {status.replace('_', ' ').title()}\n"
result += f"Priority: {priority.title()}\n"
if task[2]: # description
result += f"Description: {task[2]}\n"
result += f"ID: {task[0]}\n\n"
return result
def format_stats_display():
"""Format project statistics with visual indicators"""
stats = get_stats()
result = "## 📊 Project Statistics\n\n"
result += f"👥 **Total Users:** {stats['total_users']}\n"
result += f"📋 **Total Tasks:** {stats['total_tasks']}\n\n"
if stats['task_breakdown']:
result += "### Task Status Breakdown\n"
for status, count in stats['task_breakdown'].items():
emoji = {'todo': '📋', 'in_progress': '🔄', 'done': '✅'}.get(status, '📌')
result += f"{emoji} {status.replace('_', ' ').title()}: {count}\n"
# Display AI enhancement status
api_status = "🤖 Groq AI Enhanced" if task_parser.use_groq else "📝 Basic Parser"
result += f"\n**NLP Status:** {api_status}"
return result
Core Chatbot Logic
The main response handler processes user commands and coordinates between parsing, database operations, and response formatting.
def chatbot_response(message, history):
"""
Main chatbot response function that handles all user interactions.
Routes commands to appropriate handlers based on parsed intent.
"""
message = message.strip()
message_lower = message.lower()
# Handle task creation commands
if task_parser.is_task_creation(message):
task_info = task_parser.extract_task_info(message)
if not task_info['success']:
return f"❌ {task_info.get('error', 'Could not create task')}. Try: 'Create task: Fix login bug'"
title = task_info['title']
priority = task_info.get('priority', 'medium')
description = f"Created from: {message}"
task_id = create_task(title, description, priority)
if task_id:
priority_emoji = {'high': '🔴', 'medium': '🟡', 'low': '🟢'}.get(priority, '⚪')
result = f"✅ **Task Created Successfully!**\n\n"
result += f"📋 **Title:** {title}\n"
result += f"{priority_emoji} **Priority:** {priority.title()}\n"
result += f"🆔 **ID:** {task_id}\n"
result += f"📊 **Status:** Todo\n"
if task_parser.use_groq:
result += f"\n*🤖 Enhanced with Groq AI*"
return result
else:
return "❌ Failed to save task to database"
# Handle status update commands
elif task_parser.is_status_update(message):
info = task_parser.parse_status_update(message)
if not info:
return "❌ Could not parse status update. Try: \"change status of <task> to done\""
success = update_task_status(info["title"], info["new_status"])
if success:
return (f"✅ **Task Status Updated!**\n\n"
f"📋 **Title:** {info['title']}\n"
f"📊 **New Status:** {info['new_status'].replace('_',' ').title()}")
else:
return f"❌ No task found with title \"{info['title']}\""
# Handle information requests
elif any(word in message_lower for word in ['users', 'team', 'people']):
return format_users_display()
elif any(word in message_lower for word in ['tasks', 'work', 'jobs']):
return format_tasks_display()
elif any(word in message_lower for word in ['stats', 'statistics', 'summary']):
return format_stats_display()
# Handle greetings
elif any(word in message_lower for word in ['hello', 'hi', 'hey']):
ai_status = "🤖 Groq AI Enhanced" if task_parser.use_groq else "📝 Basic Mode"
return f"""👋 **Welcome to Project Management Chatbot!**
**Status:** {ai_status}
Commands available:
- **📋 Create Tasks**: "Create task: Fix login bug"
- **🔄 Update Status**: "Change status of Login bug to done"
- **👥 View Team**: "Show users"
- **📋 View Tasks**: "Show tasks"
- **📊 Statistics**: "Show stats"
Try: "Create task: Update documentation"
What would you like to do?"""
# Handle help requests
elif 'help' in message_lower:
return """🆘 **Help - Available Commands**
**📋 Task Management:**
- "Create task: [title]"
- "Add high priority task: [description]"
- "Change status of [task name] to [todo/in_progress/done]"
**📊 Information:**
- "Show users" or "team"
- "Show tasks" or "work"
- "Show stats" or "statistics"
**Examples:**
- "Create task: Fix login page"
- "Change status of Setup repo to done"
- "Show all tasks"
What would you like to try?"""
# Default response for unrecognized commands
else:
return f"""🤔 Command not recognized: "{message}"
**💡 Want to create a task?** Try:
- "Create task: [your description]"
**🔄 Need to update status?** Try:
- "Change status of [task name] to done"
**📊 Need information?** Try:
- "Show tasks" | "Show users" | "Show stats"
**🆘 Need help?** Type "help"
What can assist with?"""
Gradio Interface Implementation
The user interface layer creates an interactive chat experience with proper event handling and visual design.
import gradio as gr
# Create the main interface
with gr.Blocks(title="Project Management Chatbot", theme=gr.themes.Soft()) as demo:
# Header section with application description
gr.Markdown("""
# 🤖 Project Management Chatbot
**AI-Powered Task Management with Natural Language Processing**
Create tasks, view team information, and manage projects through conversation!
""")
# Display current AI enhancement status
ai_status = "🤖 **Groq AI Enhanced**" if task_parser.use_groq else "📝 **Basic Parser Mode**"
gr.Markdown(f"**Status:** {ai_status}")
# Main chat interface with welcome message
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(
value=[["Hello!", "👋 Welcome! Try: 'Create task: Fix login bug' or 'Show all tasks'"]],
height=400,
bubble_full_width=False
)
# User input section
msg = gr.Textbox(
placeholder="Type your message... (e.g., 'Create task: Fix login bug')",
label="Message"
)
# Control buttons
with gr.Row():
submit_btn = gr.Button("Send", variant="primary")
clear_btn = gr.Button("Clear", variant="secondary")
# Usage examples section
gr.Markdown("""
### 🚀 Try these examples:
- "Create task: Fix login page bug"
- "Add high priority task: Database optimization"
- "Change status of Setup repo to done"
- "Show all tasks"
- "Show team members"
- "Show project statistics"
""")
# Event handler for message processing
def respond(message, chat_history):
"""Process user message and update chat history"""
if not message.strip():
return chat_history, ""
# Add user message to history
chat_history.append([message, None])
# Generate bot response
bot_response = chatbot_response(message, chat_history)
# Add bot response to history
chat_history[-1][1] = bot_response
return chat_history, ""
# Bind events to interface components
submit_btn.click(respond, [msg, chatbot], [chatbot, msg])
msg.submit(respond, [msg, chatbot], [chatbot, msg])
clear_btn.click(lambda: [], None, chatbot)
# Launch application
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo.launch()
Hugging Face Spaces Deployment Process
Step 1: Prepare Deployment Files
Create the required configuration files for Hugging Face Spaces deployment:
README.md:
---
title: Project Management Chatbot
emoji: 🤖
colorFrom: blue
colorTo: green
sdk: gradio
sdk_version: "4.44.1"
app_file: app.py
pinned: false
license: mit
---
# Project Management Chatbot 🤖
An AI-powered project management assistant for natural language task management.
## Features
- Natural language task creation and status updates
- Team member and role management
- Project statistics and reporting
- Optional Groq AI integration for enhanced parsing
## Usage
- "Create task: Fix login bug"
- "Change status of Setup repo to done"
- "Show all tasks"
- "Show team members"
requirements.txt:
gradio==4.44.1
groq==0.4.1
Step 2: Create Hugging Face Space
- Navigate to Hugging Face Hub
- Go to huggingface.co
- Sign in to account or create new account
- Create New Space
- Click “Create new” → “Space”
- Configure space settings:
- Owner: Your username
- Space name:
project-management-chatbot - License: MIT
- SDK: Gradio
- Visibility: Public
- Click “Create Space”
Step 3: Upload Application Files
Method 1: Web Interface Upload
- In the new space, click “Upload files”
- Drag and drop or select files:
app.py(complete application code)requirements.txt(dependency specifications)README.md(space configuration and documentation)
- Add commit message: “Initial deployment of Project Management Chatbot”
- Click “Commit changes”
Method 2: Git Repository Method
# Clone space repository
git clone https://huggingface.co/spaces/your-username/project-management-chatbot
cd project-management-chatbot
# Add application files
cp /path/to/app.py .
cp /path/to/requirements.txt .
cp /path/to/README.md .
# Commit and push
git add .
git commit -m "Initial deployment"
git push
Step 4: Configure Groq API Secret
- Obtain Groq API Key
- Visit console.groq.com
- Create account and generate API key
- Copy key (format:
gsk_...)
- Add Secret to Space
- Navigate to space Settings tab
- Scroll to “Repository secrets” section
- Click “New secret”
- Enter details:
- Name:
GROQ_API_KEY - Value: Your Groq API key
- Name:
- Click “Add secret”
- Restart Space
- Click “Restart Space” button to apply secret
- Monitor build logs for successful initialization
Step 5: Monitor Deployment
- Build Process
- Watch for “Building…” status indicator
- Monitor logs for dependency installation
- Expected build time: 2-5 minutes
- Successful Deployment Indicators
- Status changes to “Running”
- Log shows: “Running on local URL: http://127.0.0.1:7860”
- Space becomes accessible via public URL
- Access Live Application
- URL format:
https://huggingface.co/spaces/your-username/project-management-chatbot - Test core functionality immediately
- URL format:
Conclusion
This implementation successfully demonstrates building and deploying a conversational AI application from initial requirements through production deployment. The project achieved its primary objective of creating a functional project management chatbot capable of natural language task creation, status updates, and comprehensive reporting.